What Are the Different Modes of Transportation in Logistics?
In the logistics industry, efficient transportation ensures seamless supply chain operations. Modes of transportation in logistics, encompassing roads, rails, seas, and air, play a pivotal role in the journey of goods. This post sheds light on the critical synergy between logistics and transportation modes, highlighting their significance in orchestrating the smooth flow of goods from origin to destination.
A] Understanding Modes of Transportation in Logistics
Understanding transportation modes in logistics is essential for efficient supply chain operations and the evolution of the logistics sector. In logistics services, these modes, including roads, rails, seas, and air, play distinct roles in the journey of goods from origin to destination.
The significance lies in their unique attributes – roads for versatility, rails for efficiency, seas for capacity, and air for speed. Different modes of transportation in logistics create a diversified network, ensuring seamless supply chain orchestration. Navigating this landscape requires a comprehensive grasp of logistics services, including fine art moving services, where each mode contributes uniquely to the efficiency and effectiveness of the overall process.
B] Five Key Modes of Transportation in Logistics
Discover how packers and movers services optimize the modes for seamless cargo movement from road and rail to sea and air. Understanding these types of transportation in logistics is pivotal for robust supply chain management. Following are the 5 modes of transportation in logistics:
1. Road Transportation
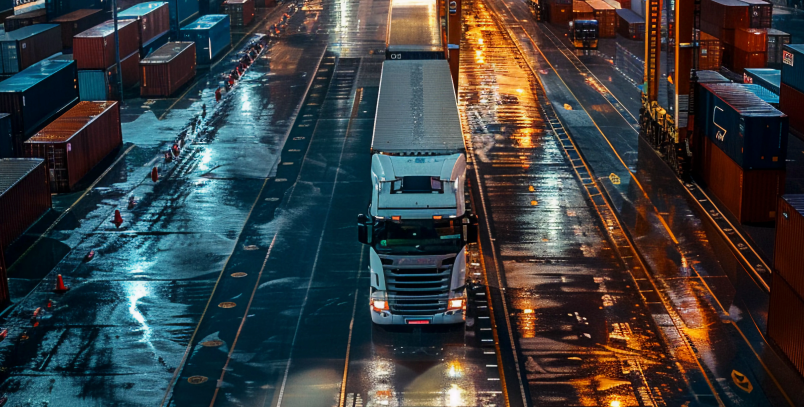

In logistics and supply chain management, understanding road transportation advantages and disadvantages is crucial for making informed decisions about cargo movement. It offers unparalleled flexibility and accessibility. Known for door-to-door delivery, road transportation services excel in shorter distances. Despite advantages like quick transit times, it faces challenges such as traffic congestion and limited capacity, yet remains crucial in logistics and supply chain management.
Advantages
Door-to-Door Delivery: Road transport eliminates the multiple handling stages and delivers from the origin to the destination.
Time-Saving: Road transport can be faster compared to rail and sea transport as it eliminates the handling and transit time.
Cost-Effective: The cost is cheaper compared to railways, ports, and airports. It also saves the handling charges.
Challenges
Traffic Congestion: Traffic can be a challenge, especially in urban areas which can cause delays.
Weather Condition: In some cases, weather conditions such as storms, fog, or heavy rain can make your deliveries delayed.
2. Rail Transportation
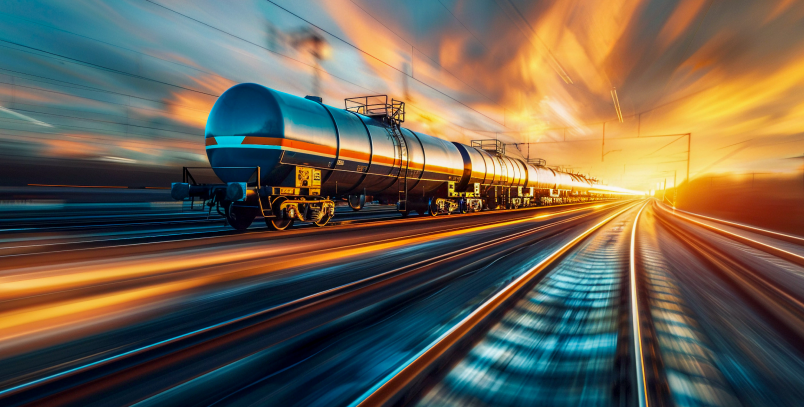

Efficient and cost-effective for bulk cargo over long distances, rail transportation minimizes environmental impact. While reliability is a key advantage, challenges include limited connectivity. In modern logistics, rail plays a vital role, particularly in transporting heavy loads in a reliable and environmentally friendly manner.
Advantages
High-capacity: Rail transport is ideal for heavy and bulky items compared to trucks, and vans. So you can move everything in a single trip. This makes it more preferable.
Cost-Effective: Rail transportation is more cost-effective for long-distance delivery as it requires less fuel cost and road maintenance costs.
Reduce Environmental Impact: Rail transport is always a greener choice for people who care about the environment as it produces less pollution for the tons of goods they carry.
Challenges
Time taking: Rail transport is more time-consuming than road or air transport. So you may face delay on deliveries.
Multiple Handling: The process of loading and unloading can increase the chances of damage.
3. Sea Transportation
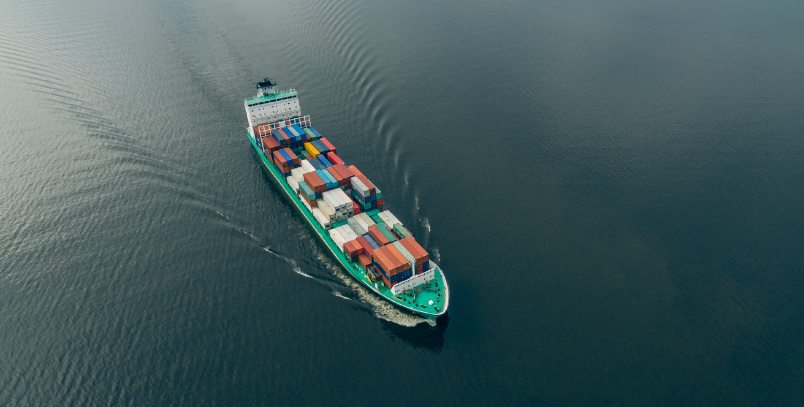

A global connector, sea transportation boasts high capacity and cost-effectiveness for long distances. Despite slower transit times and limited accessibility to certain regions, it plays a crucial and unique role in international logistics, particularly for large quantities of goods transported across oceans and continents.
Advantage
Cost Effective for Bulky Goods: It is cheaper for large and bulky goods as it reduces the per unit cost.
Capacity: Ships have a good capacity for goods like machinery, vehicles, and any other bulky material.
Global Reach: It is the best way of transport for global trade.
Challenges
Low Speed: It is the slowest mode of transportation compared to air and road transport. It is not suitable for urgent deliveries.
Weather Condition: The delivery timing can affected by the weather conditions.
4. Air Transportation

Recognized for its speed and precision, air transportation is ideal for time-sensitive logistics scenarios. With rapid delivery and a global reach, it ensures efficiency but comes with challenges like high costs and limited capacity for bulk goods, making it suitable for high-value and time-sensitive shipments.
Advantages
Fastest Mode: It is the quickest mode of transport for long distances, and is ideal for urgent delivery.
Global Reach: Air transport is helpful for international trade, it lets you deliver your high-value goods to other cities and countries faster.
Challenges
Costly: Air transport is more expensive than rail and sea transportation. It is not suitable for low-value goods.
Capacity Limit: Air transport has limited cargo space, so it allows limited goods to be transported at one time.
5. Multimodal Transportation

Multimodal transportation emphasizes combined transport methods for optimized logistics. Offering benefits such as the safety of consignments and reduced costs through optimization, it involves considerations like time for movement and extensive document work. A rising trend in modern logistics strategies, it aligns with the dynamic needs of global supply chains.
Advantages
Cost Saving: As per convenient, can select two modes of transport which are less expensive and help to save money.
Flexible: Get flexibility in route planning and select the cost-effective transport mode, whether by road, rail, sea, or air.
Challenges
Complex Coordination: It becomes difficult to understand and communicate with the different carriers and operators. This can create confusion and delay in delivery.
Handling Stages: Due to multiple handling stages, there are chances of damage.
C] Factors Influencing Mode Selection in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Factors shaping the selection of the modes of transportation in logistics and supply chain management are the following:
1. Nature of Cargo
The characteristics of goods significantly shape transportation mode choices. Perishability, fragility, size, weight, and special handling requirements impact the selection of the most suitable mode. Logistics decisions align with cargo-specific needs to ensure efficient transportation, maintain product integrity, and meet customer expectations.
2. Distance and Destinations
Distance in determining the optimal transportation mode is pivotal. Short, medium, and long distances influence the choice, considering accessibility to diverse destinations and transportation networks. Tailoring transportation modes based on distance enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness in logistics.
3. Cost Constraints and Budgeting
Cost-effectiveness is a crucial factor in mode selection. Budget considerations influence decisions, comparing operational costs of different transportation modes. Companies strategically balance expenses, aligning transportation choices with overall logistics budgets to ensure optimal resource allocation and maintain financial viability.
4. Time Sensitivity and Urgency
Time sensitivity holds great significance in transportation mode selection. Scenarios demanding rapid delivery emphasize the need for faster modes, such as air transportation. Balancing urgency with cost considerations ensures efficient logistics operations while meeting strict delivery timelines, which is particularly crucial in time-sensitive industries.
5. Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
The increasing importance of environmental factors guides transportation decisions. Companies prioritize eco-friendly options to reduce carbon footprints, aligning with sustainability goals. Considering the overall environmental impact of different transportation modes reflects a commitment to responsible logistics practices and contributes to a greener supply chain.
D] How Can Logistics Achieve the Optimal Triad: Efficiency, Cost-Efficiency, and Environmental Responsibility?
To achieve the optimal triad in logistics, companies navigate diverse modes of transport logistics. Specialized types of packers and movers offer services like office shifting services play a role in fostering efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility in logistics management.
1. Assessing Operational Efficiency
In the realm of logistics, achieving operational efficiency involves meticulous planning to meet delivery schedules, minimize delays, and ensure reliable transit times. Companies strategically evaluate transportation modes to optimize supply chain operations.
2. Cost-Effectiveness Evaluation
To determine cost-effectiveness in transportation modes, companies employ detailed strategies. This includes methodologies for comprehensive cost comparisons, taking into account factors like fuel costs, maintenance expenses, and the advantages of economies of scale.
3. Environmental Impact Assessment
Companies focus on environmental impact assessment methodologies to evaluate the ecological footprint of transportation modes. This involves calculating carbon footprints, implementing emission reduction strategies, and initiating sustainable logistics practices.
4. Decision-Making for the Optimal Balance
In the decision-making process, companies integrate factors such as operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Emphasizing the need for balance, companies strive to select transportation modes that align with specific logistics requirements, ensuring an optimal triad of efficiency, cost-efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
Further Reading:
E] Exploring Alternative Transportation Modes in Logistics
Following are the alternative transportation modes in logistics and their potential impact on supply chains and explore evolving distribution services for optimized operations:
1. Emerging Technologies in Transportation
- Drone Delivery Systems: Unleash the potential of drones for small package delivery, reaching remote areas swiftly and overcoming last-mile challenges through our home shifting services.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Dive into the efficiency of self-driving trucks, emphasizing cost reduction and their transformative impact on road transportation.
- Hyperloop and Maglev Trains: Decode high-speed freight transport using hyperloop or maglev trains, envisioning ultra-fast, sustainable, and long-distance logistics solutions.
2. Green and Sustainable Transport
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Illuminate the rising use of electric trucks, emphasizing their diminished carbon footprint and potential cost savings via renewable energy.
- Hydrogen-Powered Transport: Assess the feasibility and benefits of hydrogen fuel cells, spotlighting their potential in emission reduction and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Biofuel and Green Initiatives: Investigate biofuels from renewable sources, highlighting their eco-friendly attributes and role in fostering sustainable transport practices.
3. Innovative Concepts and Collaborative Models
- Hyper-local Logistics Solutions: Uncover crowd-shipping and collaborative platforms that optimize local delivery, utilizing shared resources to enhance efficiency and diminish congestion.
- Vertical Integration in Logistics: Examine companies vertically integrating logistics, overseeing transportation networks, warehousing, and last-mile delivery to bolster efficiency and cost control.
- Blockchain in Transportation: Examine blockchain’s role in enhancing transparency, traceability, and security in logistics, ensuring dependable documentation, and reducing fraud within supply chains.
Trust Mega Pack and Carry for seamless transportation – Book now!
Conclusion
Embracing alternative transportation modes in logistics is imperative for adapting to the ever-evolving supply chain landscape. From innovative technologies to sustainable practices, our comprehensive logistics solutions, including storage services, integrate diverse modes, ensuring a harmonious triad of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility.
Contact us today, a leading packers and movers in India, for our cutting-edge logistics services, including alternative transportation modes and reliable warehouse services that cater to the dynamic needs of modern supply chains.

Nitin O Mahipal - MD of Mega group
Nitin O Mahipal, CEO and MD of Mega Group providing Transportation, 3PL and packing and moving services has earned his MBA in Logistics and Finance from the Cardiff University, UK. He expanded MEGA's services to FMCG, Retail, Pharma, Textiles, rubber and tyre MNC’s revolutionizing customer experience with digital initiatives like the Mega App. Under his leadership, MEGA's warehouse foot print grew from 50,000 to over 12 lac square feet space, PAN India Network of branches and Fleet of trucks, with transit times slashed to hours.

