Intermodal Transportation: The Key to Efficient Supply Chains
In today’s global market, a well-organised chain supply has become essential for competition. One of the most effective strategies to compete is intermodal transportation. This method uses multiple transportation modes, including air, road, rail, and water, to move the goods from one place to another. By combining different transportation methods, companies can achieve faster deliveries, low prices, and minimal environmental impact.
In this blog, we’ll explore intermodal transportation’s meaning, the way it works, its benefits, demanding situations, and why it is essential for modern supply chains.
A] What is Intermodal Transportation?
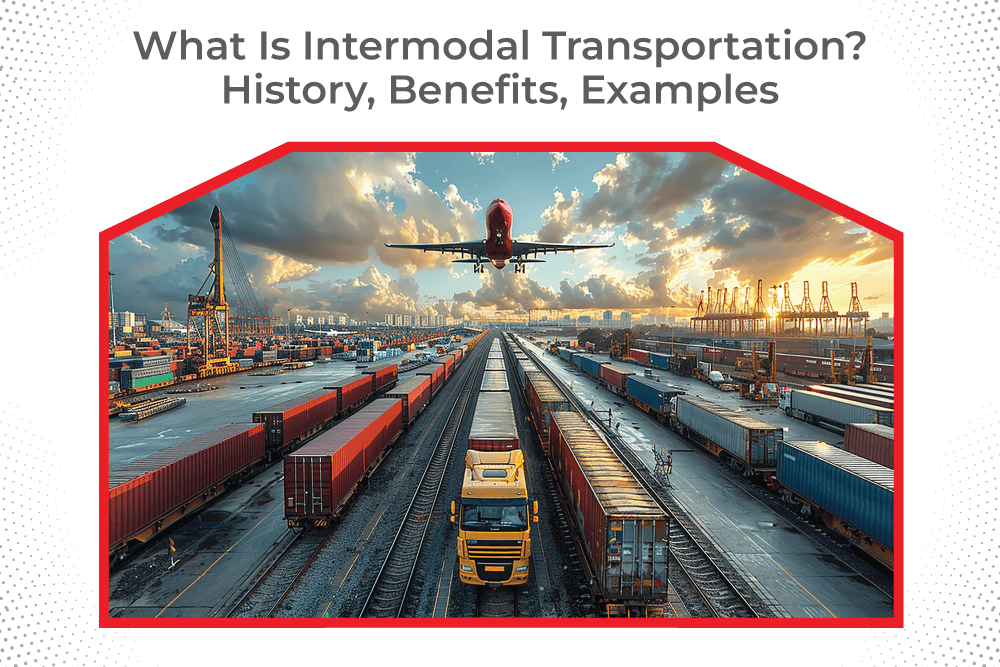
Intermodal transportation refers to the motion of products and the usage of two or more exceptional modes of transportation without managing the cargo when switching modes. This guarantees seamless delivery from the factor of origin to the final destination. This delivery approach utilises standardised boxes that can be transferred between different transportation types easily, ensuring efficiency and reducing handling costs. It’s commonly used in long-distance shipping, cross-border logistics, and transporting goods over complex routes.
Types of Transportation Used in Intermodal Shipping:
- Air: Air transportation is a good option for high-value goods as it is suitable and takes less time to transport.
- Road: This mode helps move items from factories, warehouses, or retail locations to their destination; they are utilised for transportation’s first and last stages.
- Water: A cost-effective method of transporting massive numbers of products throughout oceans and seas to other countries.
- Rail: It is an affordable option for transporting heavy cargo over long distances, as it reduces the consumption of fuel and road transport expenses.
Each delivery option is crucial in maximising supply chain efficiency by reducing costs, speeding up transit, and improving cargo safety.
B] How Intermodal Transportation Works
Intermodal transportation operates via transferring goods throughout different transport modes, normally without unpacking or directly handling the cargo. This procedure is possible because of using intermodal containers which are compatible across numerous modes of shipping.
Steps in the Intermodal Process:
- Road Transport: The journey usually begins with a truck picking up the products from the shipper’s location, such as a warehouse or factory. The truck then transports the goods to a nearby port, rail terminal, or airport.
- Rail or Water Transport: Once at the terminal, the shipment is transferred to a train or ship for the main journey. This method is normally good for the longest journey and is a more cost-effective route.
- Final Delivery: When the cargo reaches its final location, it’s transferred back to a truck for the final delivery to the final spot, such as a distribution service centre or retail shop.
C] Types of Intermodal Transportation
There are several types of intermodal transportation systems, each tailored to the requirement of the shipper, the cargo, and the distance.
- Containerised Intermodal Shipping
This is the maximum used type of intermodal transport, wherein items are packed into standard ISO boxes that can be easily transferred among ships, vans, and trains without difficulty.
- Trailer-on-Flatcar (TOFC)
It is also known as “piggybacking,” this method involves transporting truck trailers on flatbed rail cars, allowing long-haul cargo to be transported successfully via rail while decreasing road congestion.
- Double-Stack Container Shipping
This rail transport method involves stacking two containers on top of each other, maximising each train’s efficiency and capacity.
- Bulk Intermodal Transport
This mode is used for transporting bulk commodities like grain, oil, or chemicals, this method relies on specialised containers or tankers that could be shifted in different transport modes.
D] Advantages of Intermodal Transportation
Many advantages come with intermodal transportation, particularly for businesses that manage complicated or long-distance supply chains. Businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and meet customer demands by utilising multiple transport modes.
1. Reduced Costs
Businesses can minimise their average shipping costs by using multiple modes of transportation. For long-distance, rail and water transportation are usually more affordable and fuel-saving than air or road transportation. This cost savings can be helpful for the consumer, as it makes products more affordable and competitive.
2. Greater Access To Capacity
At peak delivery times or during periods of increased demand, businesses may find it challenging to secure sufficient capacity in any one mode of transportation. By allowing companies to use many modes of transportation simultaneously, intermodal transportation increases flexibility and guarantees that goods flow even during peak times. This simplifies the process of managing high or irregular shipping volumes.
3. Increased Safety
Intermodal freight transportation improves shipment safety and security. During transportation, goods are shipped in sealed containers, which minimises the chances of theft and damage. Additionally, containers are packed so well that they hardly get opened during transit, which minimises the danger of mismanagement. This makes intermodal shipping more appealing for shipping high-price or sensitive goods.
4. Sustainability
The environmental sustainability concern is growing day by day. Many businesses are switching to greener solutions for their supply chains. Intermodal transportation contributes to sustainability as this mode uses more green shipping like rails and ships, which generate less emissions than vans or airplanes. So intermodal logistics is an effective solution for businesses trying to minimise their carbon footprint during transportation by using less gasoline consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
E] Challenges in Intermodal Shipping
Just like two sides of a coin, intermodal transportation offers many benefits, and that is why there are also some challenges that businesses must consider. Successfully managing an intermodal supply chain requires overcoming various limitations. They are as follows:
1. Lack of Infrastructure
The efficiency of intermodal shipping relies closely on the availability of well-advanced infrastructure, which includes rail lines, ports, and terminals. In many regions, particularly in developing countries, insufficient infrastructure can cause delays and disruptions in the transportation procedure. Businesses might also face logistical challenges when transporting to or from areas with limited intermodal connections, leading to higher costs and longer transit times.
2. Coordination Challenges
Managing intermodal logistics requires careful coordination between a multiple service provider, including truckers, rail operators, shipping lines, and customs authorities. A breakdown in communication or delays at switching points can disrupt the complete supply chain. Businesses must work closely with transportation companions to ensure smooth transitions among modes and prevent delays or errors.
3. Security
While intermodal shipping enhances cargo security via using sealed containers, it isn’t always completely proof against safety threats. Goods are frequently transferred between various terminals, ports, and rail yards, which can expose them to risks of robbery, tampering, or smuggling. Implementing strict safety features and tracking systems is crucial to safeguarding goods throughout the journey.
Conclusion
In today’s supply chains, intermodal transportation is essential since it provides a number of advantages, such as cost savings, security, and environmental sustainability. Businesses can optimise operations and streamline their logistics for both short- and long-haul trips by utilising a variety of transportation modes, such as air, road, sea, and rail. To guarantee a simple and reliable delivery process, it’s crucial to overcome the challenges, which include infrastructure limitations, coordination issues, and safety risks.
As a packers and movers company, Mega Pack and Carry offers full logistical services, guaranteeing smooth and effective transit for all your belongings. By utilising intermodal transportation, we provide reliable, cost-effective solutions that meet the needs of both businesses and individuals. Contact us to find out how we can help you!

Nitin O Mahipal - MD of Mega group
Nitin O Mahipal, CEO and MD of Mega Group providing Transportation, 3PL and packing and moving services has earned his MBA in Logistics and Finance from the Cardiff University, UK. He expanded MEGA's services to FMCG, Retail, Pharma, Textiles, rubber and tyre MNC’s revolutionizing customer experience with digital initiatives like the Mega App. Under his leadership, MEGA's warehouse foot print grew from 50,000 to over 12 lac square feet space, PAN India Network of branches and Fleet of trucks, with transit times slashed to hours.

